|
…
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| database.md | ||
| gitlab.md | ||
| load_balancer.md | ||
| nfs.md | ||
| README.md | ||
| redis.md | ||
High Availability
GitLab supports several different types of clustering and high-availability. The solution you choose will be based on the level of scalability and availability you require. The easiest solutions are scalable, but not necessarily highly available.
Architecture
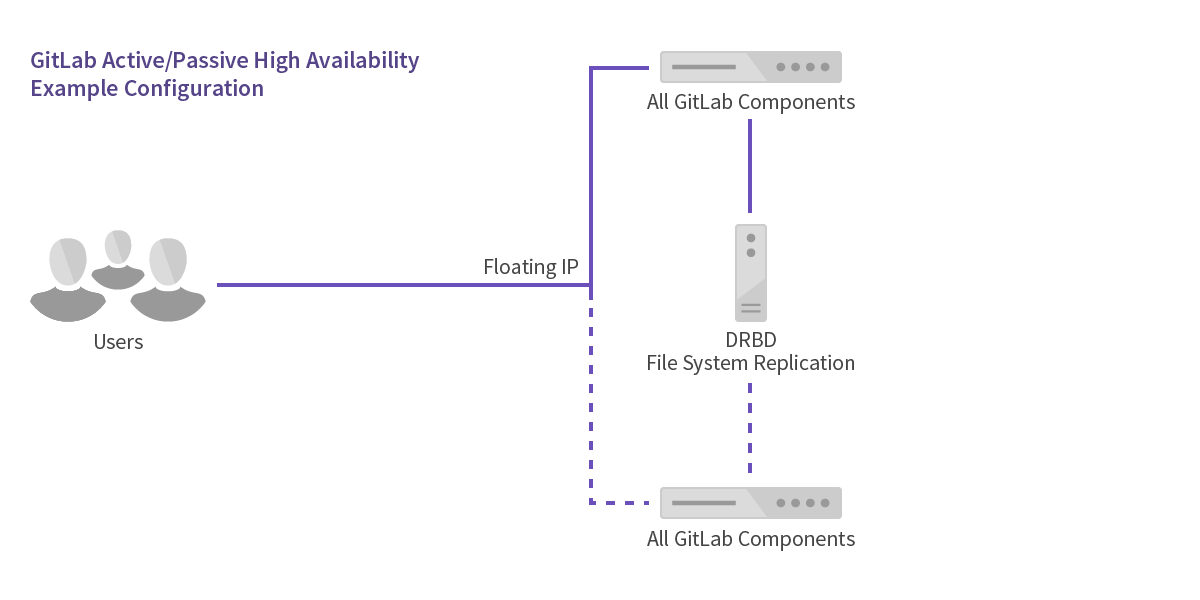
Active/Passive
For pure high-availability/failover with no scaling you can use an active/passive configuration. This utilizes DRBD (Distributed Replicated Block Device) to keep all data in sync. DRBD requires a low latency link to remain in sync. It is not advisable to attempt to run DRBD between data centers or in different cloud availability zones.
Components/Servers Required:
- 2 servers/virtual machines (one active/one passive)
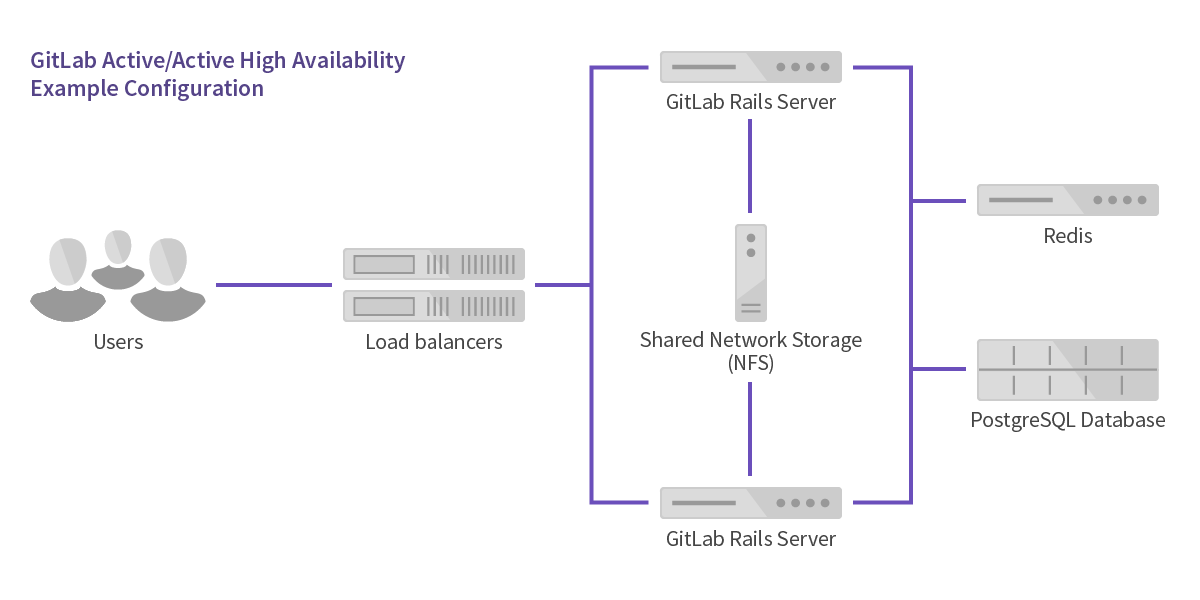
Active/Active
This architecture scales easily because all application servers handle user requests simultaneously. The database, Redis, and GitLab application are all deployed on separate servers. The configuration is only highly-available if the database, Redis and storage are also configured as such.
Steps to configure active/active: