| .. | ||
| autodeploy | ||
| build_artifacts | ||
| caching | ||
| docker | ||
| examples | ||
| img | ||
| permissions | ||
| quick_start | ||
| review_apps | ||
| runners | ||
| services | ||
| ssh_keys | ||
| triggers | ||
| variables | ||
| yaml | ||
| enable_or_disable_ci.md | ||
| environments.md | ||
| git_submodules.md | ||
| pipelines.md | ||
| README.md | ||
| comments | description |
|---|---|
| false | Learn how to use GitLab CI/CD, the GitLab built-in Continuous Integration, Continuous Deployment, and Continuous Delivery toolset to build, test, and deploy your application. |
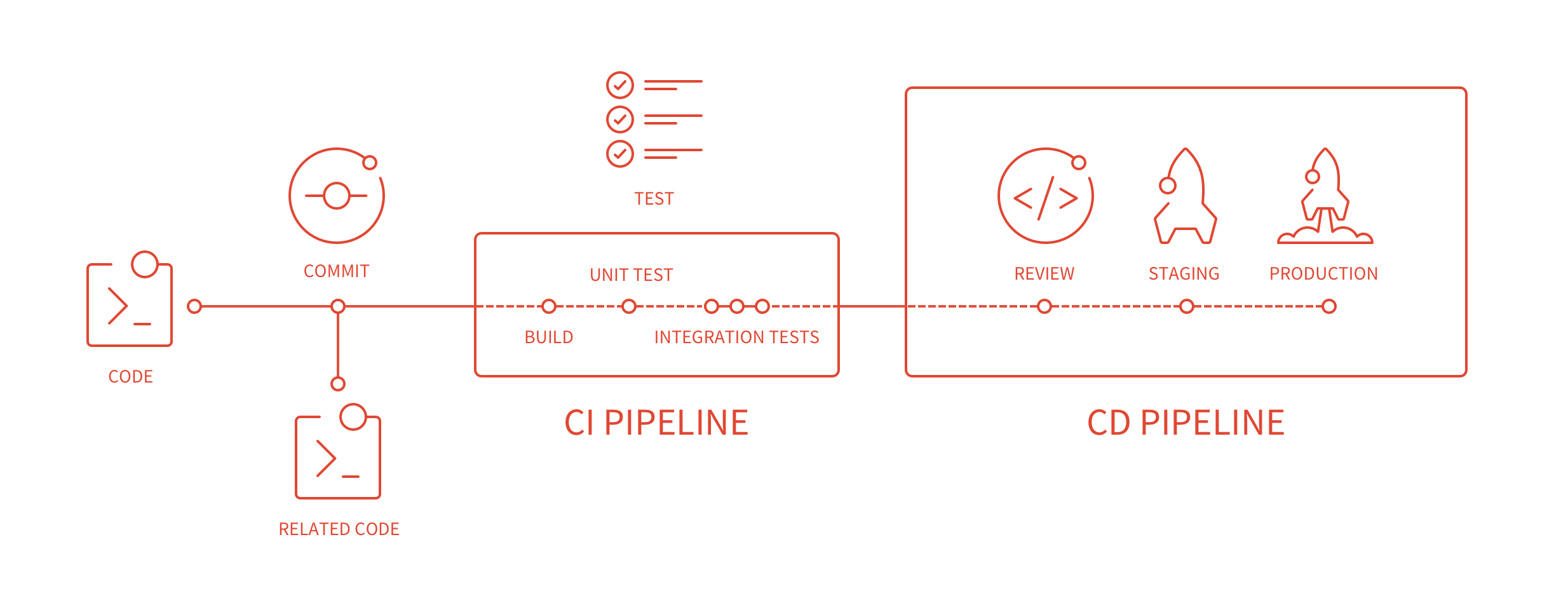
GitLab Continuous Integration (GitLab CI/CD)
The benefits of Continuous Integration are huge when automation plays an integral part of your workflow. GitLab comes with built-in Continuous Integration, Continuous Deployment, and Continuous Delivery support to build, test, and deploy your application.
Here's some info we've gathered to get you started.
Getting started
The first steps towards your GitLab CI/CD journey.
- Getting started with GitLab CI/CD: understand how GitLab CI/CD works.
- GitLab CI/CD configuration file:
.gitlab-ci.yml- Learn all about the ins and outs of.gitlab-ci.yml. - Pipelines and jobs: configure your GitLab CI/CD pipelines to build, test, and deploy your application.
- Runners: The GitLab Runner is responsible by running the jobs in your CI/CD pipeline. On GitLab.com, Shared Runners are enabled by default, so you don't need to set up anything to start to use them with GitLab CI/CD.
Introduction to GitLab CI/CD
- Article (2016-08-05): Continuous Integration, Delivery, and Deployment with GitLab - Intro to CI/CD
- Article (2015-12-14): Getting started with GitLab and GitLab CI - Intro to CI
- Article (2017-07-13): Making CI Easier with GitLab
- Article (2017-05-22): Fast and Natural Continuous Integration with GitLab CI
- Videos:
- Demo (Streamed live on Jul 17, 2017): GitLab CI/CD Deep Dive
- Demo (March, 2017): How to get started using CI/CD with GitLab
- Webcast (April, 2016): Getting started with CI in GitLab
- Third-party videos:
Why GitLab CI/CD?
- Article (2016-10-17): Why We Chose GitLab CI for our CI/CD Solution
- Article (2016-07-22): Building our web-app on GitLab CI: 5 reasons why Captain Train migrated from Jenkins to GitLab CI
Exploring GitLab CI/CD
- CI/CD Variables - Learn how to use variables defined in
your
.gitlab-ci.ymlor secured ones defined in your project's settings - The permissions model - Learn about the access levels a user can have for performing certain CI actions
- Configure a Runner, the application that runs your jobs
- Article (2016-03-01): Setting up GitLab Runner For Continuous Integration
- Article (2016-07-29): GitLab CI: Run jobs sequentially, in parallel, or build a custom pipeline
- Article (2016-08-26): GitLab CI: Deployment & environments
- Article (2016-05-23): Introduction to GitLab Container Registry
Advanced use
Once you get familiar with the basics of GitLab CI/CD, it's time to dive in and learn how to leverage its potential even more.
- Environments and deployments: Separate your jobs into environments and use them for different purposes like testing, building and deploying
- Job artifacts
- Caching dependencies
- Git submodules - How to run your CI jobs when Git submodules are involved
- Use SSH keys in your build environment
- Trigger pipelines through the GitLab API
- Trigger pipelines on a schedule
- Kubernetes clusters - Integrate one or more Kubernetes clusters to your project
GitLab CI/CD for Docker
Leverage the power of Docker to run your CI pipelines.
- Use Docker images with GitLab Runner
- Use CI to build Docker images
- CI services (linked Docker containers)
- Article (2016-03-01): Setting up GitLab Runner For Continuous Integration
Review Apps
- Review Apps documentation
- Article (2016-11-22): Introducing Review Apps
- Example project that shows how to use Review Apps
Auto DevOps
- Auto DevOps: Auto DevOps automatically detects, builds, tests, deploys, and monitors your applications.
GitLab CI for GitLab Pages
See the documentation on GitLab Pages.
Examples
Check the GitLab CI/CD examples for a collection of tutorials and guides on setting up your CI/CD pipeline for various programming languages, frameworks, and operating systems.
Integrations
- Article (2016-06-09): Continuous Delivery with GitLab and Convox
- Article (2016-05-05): Getting Started with GitLab and Shippable Continuous Integration
- Article (2016-04-19): GitLab Partners with DigitalOcean to make Continuous Integration faster, safer, and more affordable
Special configuration (GitLab admin)
As a GitLab administrator, you can change the default behavior of GitLab CI/CD in your whole GitLab instance as well as in each project.
- Continuous Integration admin settings
- Project specific:
- Affecting the whole GitLab instance:
Breaking changes
- CI variables renaming for GitLab 9.0 Read about the deprecated CI variables and what you should use for GitLab 9.0+.
- New CI job permissions model Read about what changed in GitLab 8.12 and how that affects your jobs. There's a new way to access your Git submodules and LFS objects in jobs.