|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .. | ||
| autodeploy | ||
| build_artifacts | ||
| caching | ||
| chatops | ||
| docker | ||
| examples | ||
| img | ||
| interactive_web_terminal | ||
| merge_request_pipelines | ||
| permissions | ||
| quick_start | ||
| review_apps | ||
| runners | ||
| services | ||
| ssh_keys | ||
| triggers | ||
| variables | ||
| yaml | ||
| enable_or_disable_ci.md | ||
| environments.md | ||
| git_submodules.md | ||
| junit_test_reports.md | ||
| pipelines.md | ||
| README.md | ||
| comments | description |
|---|---|
| false | Learn how to use GitLab CI/CD, the GitLab built-in Continuous Integration, Continuous Deployment, and Continuous Delivery toolset to build, test, and deploy your application. |
GitLab Continuous Integration (GitLab CI/CD)
GitLab provides tools for continuously integrating and delivering code.
Within the entire DevOps lifecycle, GitLab CI/CD spans the Verify (CI) and Release (CD) stages.
Overview
CI/CD is a vast area, so GitLab provides documentation for all levels of expertise. Consult the following table to find the right documentation for you:
| Level of expertise | Resource |
|---|---|
| New to the concepts of CI and CD | For a high-level overview, see the GitLab Continuous Integration & Delivery product page. |
| Familiar with the purpose of CI/CD | Delve into GitLab CI/CD by continuing down the page, starting with our introduction. |
| Familiar with GitLab CI/CD concepts | After getting familiar with GitLab CI/CD, let us walk you through a simple example in our quick start guide. |
| A GitLab CI/CD expert | Jump straight to our .gitlab.yml reference. |
Introduction
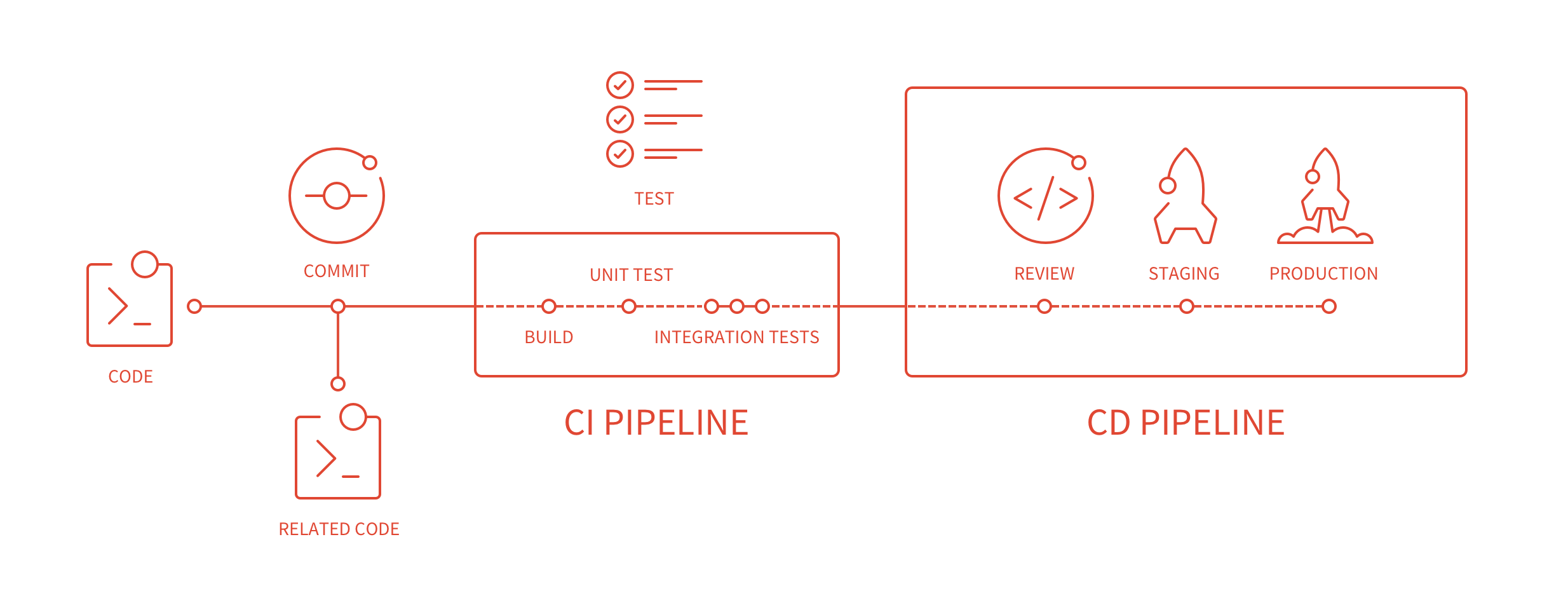
The following introduces the process of continuous integration (CI) and continuous delivery (CD):
In this illustration:
- New code is combined with existing code through a commit to a project's repository.
- The newly combined code is sent to a CI pipeline where:
- The code is built.
- Unit and integration tests are run over the built code.
- Assuming the build and tests are successful, a CD pipeline is triggered to allow for:
- Review using Review Apps.
- Deploying to configured environments.
The benefits of CI/CD are vast, allowing automation to be an integral part of your workflow for testing, building, deploying, and monitoring your code.
Because CI and CD with GitLab is broad topic with many possibilities, the rest of this section provides links to topics and resources needed to make use of GitLab CI/CD.
Essentials
The following documentation provides the minimum required knowledge for making use of GitLab CI/CD:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Getting started with GitLab CI/CD | Outlines the first steps for configuring GitLab CI/CD. |
| Introduction to pipelines and jobs | Provides an overview of GitLab CI/CD and jobs. |
Configuration of your pipelines with .gitlab-ci.yml |
A comprehensive reference for the .gitlab-ci.yml file. |
NOTE: Note: Familiarity with GitLab Runner is useful because it is responsible for running the jobs in your CI/CD pipeline. On GitLab.com, shared Runners are enabled by default so you don't need to set up anything to get started.
Auto DevOps
An alternative to manually configuring CI/CD, GitLab supports Auto DevOps, which:
- Provides simplified setup and execution of CI/CD.
- Allows GitLab to automatically detect, build, test, deploy, and monitor your applications.
Basic usage
With basic knowledge of how GitLab CI/CD works, the following documentation extends your knowledge into more features:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| CI/CD Variables | How environment variables can be configured and made available in pipelines. |
| Where variables can be used | A deeper look into where and how CI/CD variables can be used. |
| User and job permissions | Learn about the access levels a user can have for performing certain CI actions. |
| Configuring GitLab Runners | Documentation for configuring GitLab Runner. |
Advanced usage
Once you get familiar with the basics of GitLab CI/CD, consult the following documentation to make use of advanced features:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Introduction to environments and deployments | Learn how to separate your jobs into environments and use them for different purposes like testing, building and, deploying. |
| Job artifacts | Learn about the output of jobs. |
| Cache dependencies in GitLab CI/CD | Discover how to speed up pipelines using caching. |
| Using Git submodules with GitLab CI | How to run your CI jobs when using Git submodules. |
| Pipelines for merge requests | Create pipelines specifically for merge requests. |
| Using SSH keys with GitLab CI/CD | Use SSH keys in your build environment. |
| Triggering pipelines through the API | Use the GitLab API to trigger a pipeline. |
| Pipeline schedules | Trigger pipelines on a schedule. |
| Connecting GitLab with a Kubernetes cluster | Integrate one or more Kubernetes clusters to your project. |
| ChatOps | Trigger CI jobs from chat, with results sent back to the channel. |
| Interactive web terminals | Open an interactive web terminal to debug the running jobs. |
GitLab Pages
GitLab CI/CD can be used to build and host static websites. For more information, see the documentation on GitLab Pages.
Examples
Check out the GitLab CI/CD examples for a collection of tutorials and guides on setting up your CI/CD pipeline for various programming languages, frameworks, and operating systems.
Administration
As a GitLab administrator, you can change the default behavior of GitLab CI/CD for:
- An entire GitLab instance.
- Specific projects, using pipelines settings.
See also:
Using Docker
Docker is commonly used with GitLab CI/CD. Learn more about how to to accomplish this with the following documentation:
| Topic | Description |
|---|---|
| Using Docker images | Use GitLab and GitLab Runner with Docker to build and test applications. |
| Building Docker images with GitLab CI/CD | Maintain Docker-based projects using GitLab CI/CD. |
Related topics include:
- Docker integration.
- CI services (linked Docker containers).
- Setting up GitLab Runner For Continuous Integration (article).
Further resources
This section provides further resources to help you get familiar with GitLab CI/CD.
Articles
The following table provides a list of articles about CI/CD, sorted in reverse chronological order of publish date:
| Publish Date | Article |
|---|---|
| 2017-07-13 | Making CI easier with GitLab. |
| 2017-05-22 | Fast and natural continuous integration with GitLab CI. |
| 2016-11-22 | Introducing Review Apps. |
| 2016-08-26 | GitLab CI: Deployment & Environments. |
| 2016-08-05 | Continuous Integration, Delivery, and Deployment with GitLab. |
| 2016-07-29 | GitLab CI: Run jobs sequentially, in parallel or build a custom pipeline. |
| 2016-06-09 | Continuous Delivery with GitLab and Convox |
| 2016-05-23 | GitLab Container Registry. |
| 2016-05-05 | Getting Started with GitLab and Shippable Continuous Integration |
| 2016-04-19 | GitLab Partners with DigitalOcean to make Continuous Integration faster, safer, and more affordable |
| 2015-03-01 | Setting up GitLab Runner For Continuous Integration. |
| 2015-12-14 | Getting started with GitLab and GitLab CI. |
Videos
The following table provides a list of videos about CI/CD, sorted in reverse chronological order of publish date:
| Publish Date | Video |
|---|---|
| 2017-07-17 | GitLab CI/CD Deep Dive. |
| 2017-03-13 | Demo: CI/CD with GitLab in action. |
| 2016-04-20 | Webcast Recording and Slides: Getting started with CI in GitLab. |
In addition, the following third-party videos are available:
Example Projects
review-apps-nginx provides an example of using Review Apps.
Other example projects are available at the gitlab-examples group.
Why GitLab CI/CD?
The following articles explain reasons why you might use GitLab CI/CD for your CI/CD infrastructure:
See also the Why CI/CD? presentation.
Breaking changes
As GitLab CI/CD has evolved, certain breaking changes have been necessary. These are:
- CI variables renaming for GitLab 9.0. Read about the deprecated CI variables and what you should use for GitLab 9.0+.
- New CI job permissions model. See what changed in GitLab 8.12 and how that affects your jobs. There's a new way to access your Git submodules and LFS objects in jobs.