3.9 KiB
Pipeline Schedules
Notes:
- This feature was introduced in 9.1 as Trigger Schedule.
- In 9.2, the feature was renamed to Pipeline Schedule.
- Cron notation is parsed by Fugit.
Pipeline schedules can be used to run a pipeline at specific intervals, for example every month on the 22nd for a certain branch.
Using Pipeline schedules
In order to schedule a pipeline:
- Navigate to your project's CI / CD ➔ Schedules and click the New Schedule button.
- Fill in the form
- Hit Save pipeline schedule for the changes to take effect.
Attention: The pipelines won't be executed precisely, because schedules are handled by Sidekiq, which runs according to its interval. See advanced admin configuration for more information.
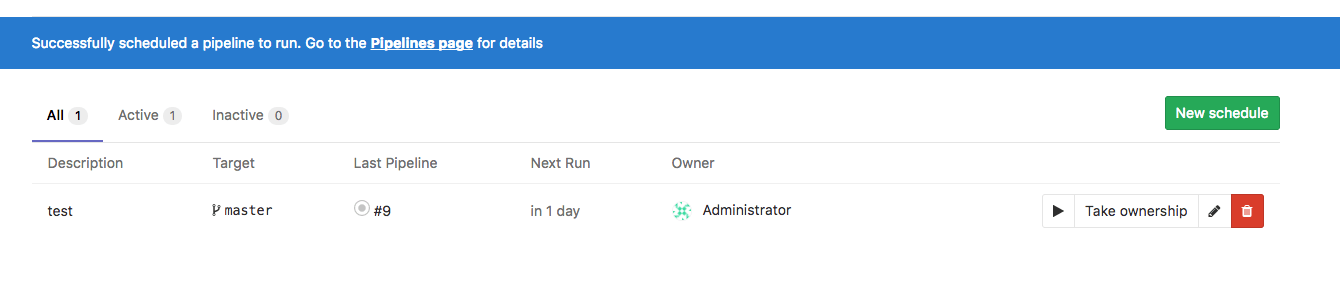
In the Schedules index page you can see a list of the pipelines that are scheduled to run. The next run is automatically calculated by the server GitLab is installed on.
Running a scheduled pipeline manually
Introduced in GitLab 10.4.
To trigger a pipeline schedule manually, click the "Play" button:
This will schedule a background job to run the pipeline schedule. A flash message will provide a link to the CI/CD Pipeline index page.
To help avoid abuse, users are rate limited to triggering a pipeline once per minute.
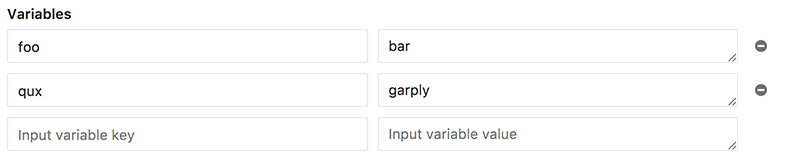
Making use of scheduled pipeline variables
Introduced in GitLab 9.4.
You can pass any number of arbitrary variables and they will be available in
GitLab CI so that they can be used in your .gitlab-ci.yml file.
Using only and except
To configure that a job can be executed only when the pipeline has been scheduled (or the opposite), you can use only and except configuration keywords.
job:on-schedule:
only:
- schedules
script:
- make world
job:
except:
- schedules
script:
- make build
Taking ownership
Pipelines are executed as a user, who owns a schedule. This influences what projects and other resources the pipeline has access to. If a user does not own a pipeline, you can take ownership by clicking the Take ownership button. The next time a pipeline is scheduled, your credentials will be used.
NOTE: Note: If the owner of a pipeline schedule doesn't have the ability to create pipelines on the target branch, the schedule will stop creating new pipelines. This can happen if, for example, the owner is blocked or removed from the project, or the target branch or tag is protected. In this case, someone with sufficient privileges must take ownership of the schedule.
Advanced admin configuration
The pipelines won't be executed precisely, because schedules are handled by
Sidekiq, which runs according to its interval. For example, if you set a
schedule to create a pipeline every minute (* * * * *) and the Sidekiq worker
runs on 00:00 and 12:00 every day (0 */12 * * *), only 2 pipelines will be
created per day. To change the Sidekiq worker's frequency, you have to edit the
pipeline_schedule_worker_cron value in your gitlab.rb and restart GitLab.
For GitLab.com, you can check the dedicated settings page. If you
don't have admin access to the server, ask your administrator.