1.6 KiB
GitLab Kubernetes / OpenShift integration
GitLab can be configured to interact with Kubernetes, or other systems using the Kubernetes API (such as OpenShift).
Each project can be configured to connect to a different Kubernetes cluster, see the configuration section.
If you have a single cluster that you want to use for all your projects, you can pre-fill the settings page with a default template. To configure the template, see the Services Templates document.
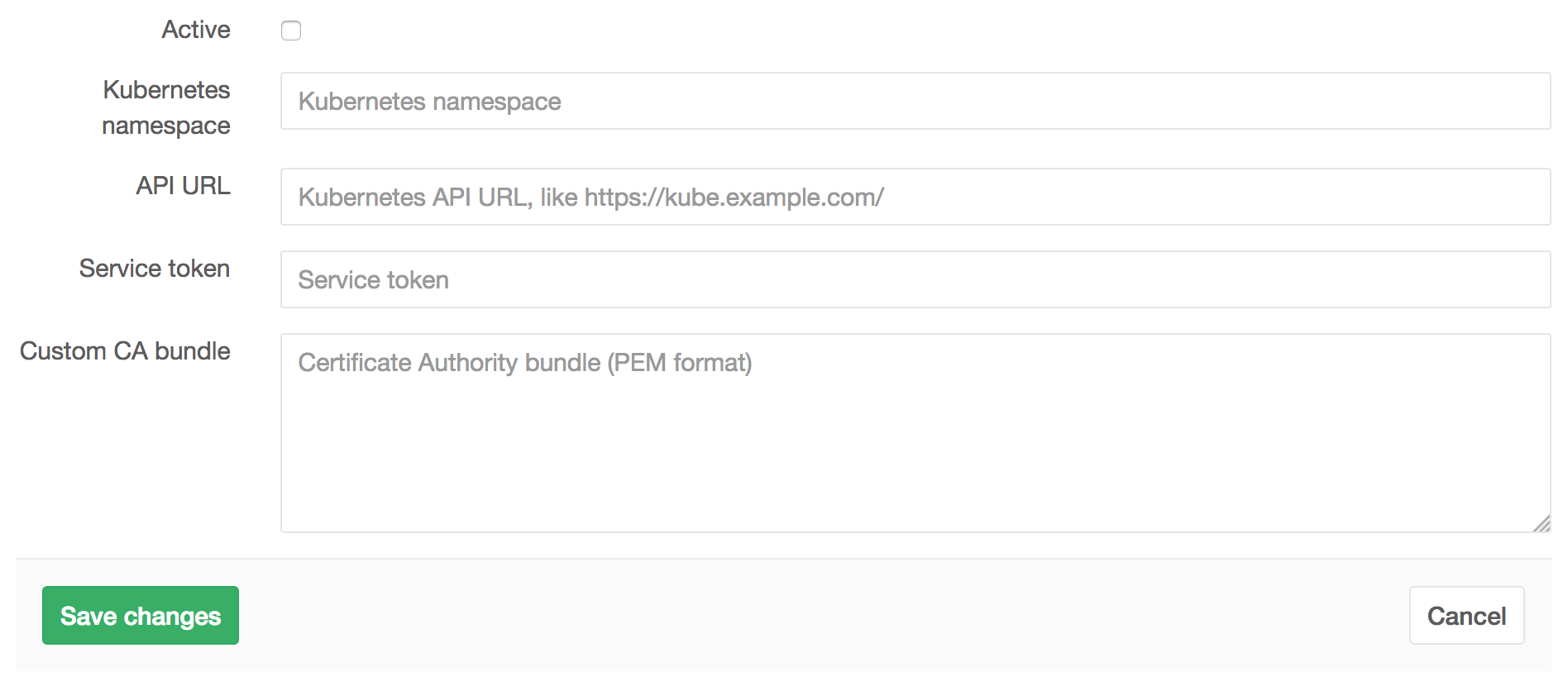
Configuration
The Kubernetes service takes the following arguments:
- Kubernetes namespace
- API URL
- Service token
- Custom CA bundle
The API URL is the URL that GitLab uses to access the Kubernetes API. Kubernetes
exposes several APIs - we want the "base" URL that is common to all of them,
e.g., https://kubernetes.example.com rather than https://kubernetes.example.com/api/v1.
GitLab authenticates against Kubernetes using service tokens, which are
scoped to a particular namespace. If you don't have a service token yet,
you can follow the
Kubernetes documentation
to create one. You can also view or create service tokens in the
Kubernetes dashboard - visit
Config -> Secrets.
Fill in the service token and namespace according to the values you just got.
If the API is using a self-signed TLS certificate, you'll also need to include
the ca.crt contents as the Custom CA bundle.