6.8 KiB
Jenkins CI service (STARTER)
Note: In GitLab 8.3, Jenkins integration using the GitLab Hook Plugin was deprecated in favor of the GitLab Plugin. The deprecated integration has been renamed to Jenkins CI (Deprecated) in the project service settings. We may remove this in a future release and recommend using the new 'Jenkins CI' project service instead which is described in this document.
Overview
Jenkins is a great Continuous Integration tool, similar to our built-in GitLab CI.
GitLab's Jenkins integration allows you to trigger a Jenkins build when you push code to a repository, or when a merge request is created. Additionally, it shows the pipeline status on merge requests widgets and on the project's home page.
Videos are also available on GitLab workflow with Jira issues and Jenkins pipelines and Migrating from Jenkins to GitLab.
Use cases
- Suppose you are new to GitLab, and want to keep using Jenkins until you prepare your projects to build with GitLab CI/CD. You set up the integration between GitLab and Jenkins, then you migrate to GitLab CI later. While you organize yourself and your team to onboard GitLab, you keep your pipelines running with Jenkins, but view the results in your project's repository in GitLab.
- Your team uses Jenkins Plugins for other proceedings, therefore, you opt for keep using Jenkins to build your apps. Show the results of your pipelines directly in GitLab.
For a real use case, read the blog post Continuous integration: From Jenkins to GitLab using Docker.
NOTE: Moving from a traditional CI plug-in to a single application for the entire software development lifecycle can decrease hours spent on maintaining toolchains by 10% or more. Visit the 'GitLab vs. Jenkins' comparison page to learn how our built-in CI compares to Jenkins.
Requirements
- Jenkins GitLab Plugin
- Jenkins Git Plugin
- Git clone access for Jenkins from the GitLab repository
- GitLab API access to report build status
Configure GitLab users
Create a user or choose an existing user that Jenkins will use to interact through the GitLab API. This user will need to be a global Admin or added as a member to each Group/Project. Developer permission is required for reporting build status. This is because a successful build status can trigger a merge when 'Merge when pipeline succeeds' feature is used. Some features of the GitLab Plugin may require additional privileges. For example, there is an option to accept a merge request if the build is successful. Using this feature would require developer, maintainer or owner-level permission.
Copy the private API token from Profile Settings -> Account. You will need this when configuring the Jenkins server later.
Configure the Jenkins server
Install Jenkins GitLab Plugin and Jenkins Git Plugin.
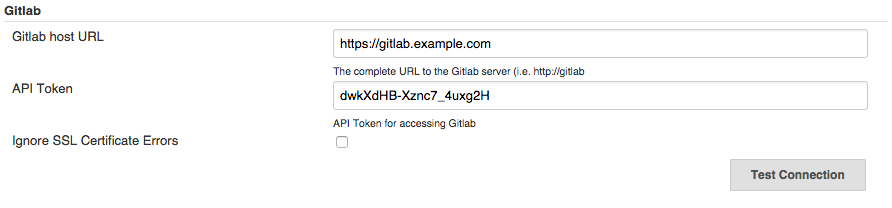
Go to Manage Jenkins -> Configure System and scroll down to the 'GitLab' section. Enter the GitLab server URL in the 'GitLab host URL' field and paste the API token copied earlier in the 'API Token' field.
For more information, see GitLab Plugin documentation about Jenkins-to-GitLab authentication
Configure a Jenkins project
Follow the GitLab Plugin documentation about Jenkins Job Configuration.
NOTE: Note: Be sure to include the steps about Build status configuration. The 'Publish build status to GitLab' post-build step is required to view Jenkins build status in GitLab Merge Requests.
Configure a GitLab project
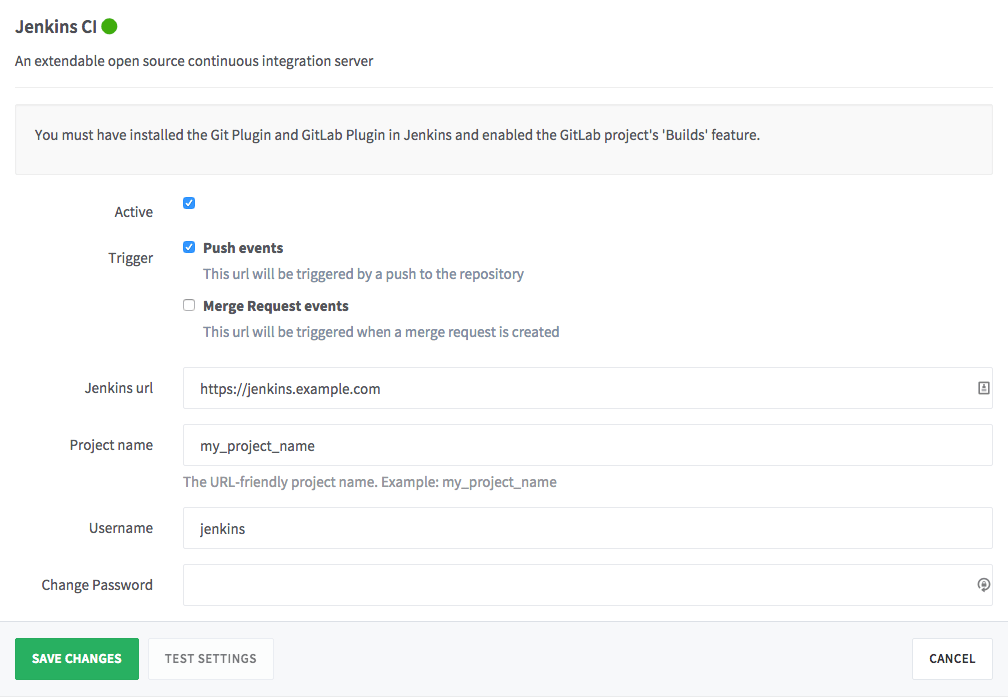
Create a new GitLab project or choose an existing one. Then, go to Integrations -> Jenkins CI.
Check the 'Active' box. Select whether you want GitLab to trigger a build on push, Merge Request creation, tag push, or any combination of these. We recommend unchecking 'Merge Request events' unless you have a specific use-case that requires re-building a commit when a merge request is created. With 'Push events' selected, GitLab will build the latest commit on each push and the build status will be displayed in the merge request.
Enter the Jenkins URL and Project name. The project name should be URL-friendly where spaces are replaced with underscores. To be safe, copy the project name from the URL bar of your browser while viewing the Jenkins project.
Optionally, enter a username and password if your Jenkins server requires authentication.
Plugin functional overview
GitLab does not contain a database table listing commits. Commits are always read from the repository directly. Therefore, it is not possible to retain the build status of a commit in GitLab. This is overcome by requesting build information from the integrated CI tool. The CI tool is responsible for creating and storing build status for Commits and Merge Requests.
Steps required to implement a similar integration
Note: All steps are implemented using AJAX requests on the merge request page.
- In order to display the build status in a merge request you must create a project service in GitLab.
- Your project service will do a (JSON) query to a URL of the CI tool with the SHA1 of the commit.
- The project service builds this URL and payload based on project service settings and knowledge of the CI tool.
- The response is parsed to give a response in GitLab (success/failed/pending).
Troubleshooting
Error in merge requests - "Could not connect to the CI server"
This integration relies on Jenkins reporting the build status back to GitLab via the Commit Status API.
The error 'Could not connect to the CI server' usually means that GitLab did not receive a build status update via the API. Either Jenkins was not properly configured or there was an error reporting the status via the API.
- Configure the Jenkins server for GitLab API access
- Configure a Jenkins project, including the 'Publish build status to GitLab' post-build action.