14 KiB
| stage | group | comments | description |
|---|---|---|---|
| none | unassigned | false | Next Runner Auto-scaling Architecture |
Next Runner Auto-scaling Architecture
Summary
GitLab Runner is a core component of GitLab CI/CD. It makes it possible to run CI/CD jobs in a reliable and concurrent environment. It has been initially introduced by Kamil Trzciński in early 2015 to replace a Ruby version of the same service. GitLab Runner written in Go turned out to be easier to use by the wider community, it was more efficient and reliable than the previous, Ruby-based, version.
In February 2016 Kamil Trzciński implemented an auto-scaling feature to leverage cloud infrastructure to run many CI/CD jobs in parallel. This feature has become a foundation supporting CI/CD adoption on GitLab.com over the years, where we now run around 4 million builds per day at peak.
During the initial implementation a decision was made to use Docker Machine:
Is easy to use. Is well documented. Is well supported and constantly extended. It supports almost any cloud provider or virtualization infrastructure. We need minimal amount of changes to support Docker Machine: machine enumeration and inspection. We don't need to implement any "cloud specific" features.
This design choice was crucial for the GitLab Runner success. Since that time the auto-scaling feature has been used by many users and customers and enabled rapid growth of CI/CD adoption on GitLab.com.
We can not, however, continue using Docker Machine. Work on that project was paused in July 2018 and there was no development made since that time (except for some highly important security fixes). In 2018, after Docker Machine entered the “maintenance mode”, we decided to create our own fork to be able to keep using this and ship fixes and updates needed for our use case. On September 26th, 2021 the project got archived and the documentation for it has been removed from the official page. This means that the original reason to use Docker Machine is no longer valid too.
To keep supporting our customers and the wider community we need to design a new mechanism for GitLab Runner auto-scaling. It not only needs to support auto-scaling, but it also needs to do that in the way to enable us to build on top of it to improve efficiency, reliability and availability.
We call this new mechanism the “next GitLab Runner Scaling architecture”.
Disclaimer The following contain information related to upcoming products, features, and functionality.
It is important to note that the information presented is for informational purposes only. Please do not rely on this information for purchasing or planning purposes.
As with all projects, the items mentioned in this document and linked pages are subject to change or delay. The development, release and timing of any products, features, or functionality remain at the sole discretion of GitLab Inc.
Proposal
Currently, GitLab Runner auto-scaling can be configured in a few ways. Some customers are successfully using an auto-scaled environment in Kubernetes. We know that a custom and unofficial GitLab Runner version has been built to make auto-scaling on Kubernetes more reliable. We recognize the importance of having a really good Kubernetes solution for running multiple jobs in parallel, but refinements in this area are out of scope for this architectural initiative.
We want to focus on resolving problems with Docker Machine and replacing this mechanism with a reliable and flexible mechanism. We might be unable to build a drop-in replacement for Docker Machine, as there are presumably many reasons why it has been deprecated. It is very difficult to maintain compatibility with so many cloud providers, and it seems that Docker Machine has been deprecated in favor of Docker Desktop, which is not a viable replacement for us. This issue contains a discussion about how people are using Docker Machine right now, and it seems that GitLab CI is one of the most frequent reasons for people to keep using Docker Machine.
There is also an opportunity in being able to optionally run multiple jobs in a single, larger virtual machine. We can’t do that today, but we know that this can potentially significantly improve efficiency. We might want to build a new architecture that makes it easier and allows us to test how efficient it is with PoCs. Running multiple jobs on a single machine can also make it possible to reuse what we call a “sticky context” - a space for build artifacts / user data that can be shared between job runs.
💡 Design a simple abstraction that users will be able to build on top of
Because there is no viable replacement and we might be unable to support all cloud providers that Docker Machine used to support, the key design requirement is to make it really simple and easy for the wider community to write a custom GitLab auto-scaling plugin, whatever cloud provider they might be using. We want to design a simple abstraction that users will be able to build on top, as will we to support existing workflows on GitLab.com.
The designed mechanism should abstract what Docker Machine executor has been doing: providing a way to create an external Docker environment, waiting to execute jobs by provisioning this environment and returning credentials required to perform these operations.
The new plugin system should be available for all major platforms: Linux, Windows, MacOS.
💡 Migrate existing Docker Machine solution to a plugin
Once we design and implement the new abstraction, we should be able to migrate existing Docker Machine mechanisms to a plugin. This will make it possible for users and customers to immediately start using the new architecture, but still keep their existing workflows and configuration for Docker Machine. This will give everyone time to migrate to the new architecture before we drop support for the legacy auto-scaling entirely.
💡 Build plugins for AWS, Google Cloud Platform and Azure
Although we might be unable to add support for all the cloud providers that Docker Machine used to support, it seems to be important to provide GitLab-maintained plugins for the major cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud Platform and Azure.
We should build them, presumably in separate repositories, in a way that they are easy to contribute to, fork, modify for certain needs the wider community team members might have. It should be also easy to install a new plugin without the need of rebuilding GitLab Runner whenever it happens.
💡 Write a solid documentation about how to build your own plugin
It is important to show users how to build an auto-scaling plugin, so that they can implement support for their own cloud infrastructure.
Building new plugins should be simple, and with the support of great documentation it should not require advanced skills, like understanding how gRPC works. We want to design the plugin system in a way that the entry barrier for contributing new plugins is very low.
💡 Build a PoC to run multiple builds on a single machine
We want to better understand what kind of efficiency can running multiple jobs on a single machine bring. It is difficult to predict that, so ideally we should build a PoC that will help us to better understand what we can expect from this.
To run this experiment we most likely we will need to build an experimental plugin, that not only allows us to schedule running multiple builds on a single machine, but also has a set of comprehensive metrics built into it, to make it easier to understand how it performs.
Details
How the abstraction for the custom provider will look exactly is something that we will need to prototype, PoC and decide in a data-informed way. There are a few proposals that we should describe in detail, develop requirements for, PoC and score. We will choose the solution that seems to support our goals the most.
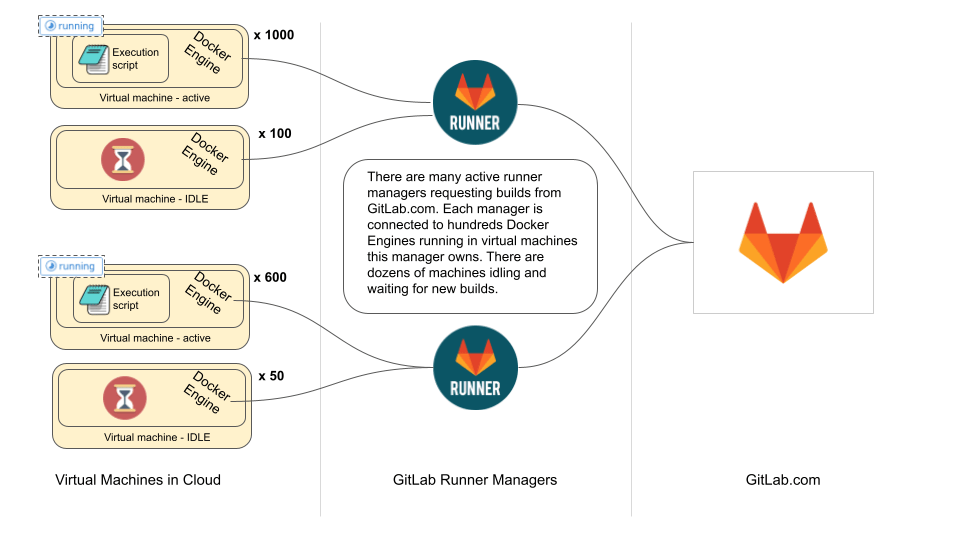
In order to describe the proposals we first need to better explain what part of the GitLab Runner needs to be abstracted away. To make this easier to grasp these concepts, let's take a look at the current auto-scaling architecture and sequence diagram.
On the diagrams above we see that currently a GitLab Runner Manager runs on a machine that has access to a cloud provider’s API. It is using Docker Machine to provision new Virtual Machines with Docker Engine installed and it configures the Docker daemon there to allow external authenticated requests. It stores credentials to such ephemeral Docker environments on disk. Once a machine has been provisioned and made available for GitLab Runner Manager to run builds, it is using one of the existing executors to run a user-provided script. In auto-scaling, this is typically done using Docker executor.
Custom provider
In order to reduce the scope of work, we only want to introduce the new abstraction layer in one place.
A few years ago we introduced the Custom Executor feature in GitLab Runner. It allows users to design custom build execution methods. The custom executor driver can be implemented in any way - from a simple shell script to a dedicated binary - that is then used by a Runner through os/exec system calls.
Thanks to the custom executor abstraction there is no more need to implement new executors internally in Runner. Users who have specific needs can implement their own drivers and don’t need to wait for us to make their work part of the “official” GitLab Runner. As each driver is a separate project, it also makes it easier to create communities around them, where interested people can collaborate together on improvements and bug fixes.
We want to design the new Custom Provider to replicate the success of the Custom Executor. It will make it easier for users to build their own ways to provide a context and an environment in which a build will be executed by one of the Custom Executors.
There are multiple solutions to implementing a custom provider abstraction. We can use raw Go plugins, Hashcorp’s Go Plugin, HTTP interface or gRPC based facade service. There are many solutions, and we want to choose the most optimal one. In order to do that, we will describe the solutions in a separate document, define requirements and score the solution accordingly. This will allow us to choose a solution that will work best for us and the wider community.
Design principles
Our goal is to design a GitLab Runner plugin system interface that is flexible and simple for the wider community to consume. As we cannot build plugins for all cloud platforms, we want to ensure a low entry barrier for anyone who needs to develop a plugin. We want to allow everyone to contribute.
To achieve this goal, we will follow a few critical design principles. These principles will guide our development process for the new plugin system abstraction.
General high-level principles
- Design the new auto-scaling architecture aiming for having more choices and flexibility in the future, instead of imposing new constraints.
- Design the new auto-scaling architecture to experiment with running multiple jobs in parallel, on a single machine.
- Design the new provisioning architecture to replace Docker Machine in a way that the wider community can easily build on top of the new abstractions.
Principles for the new plugin system
- Make the entry barrier for writing a new plugin low.
- Developing a new plugin should be simple and require only basic knowledge of a programming language and a cloud provider's API.
- Strive for a balance between the plugin system's simplicity and flexibility. These are not mutually exclusive.
- Abstract away as many technical details as possible but do not hide them completely.
- Build an abstraction that serves our community well but allows us to ship it quickly.
- Invest in a flexible solution, avoid one-way-door decisions, foster iteration.
- When in doubts err on the side of making things more simple for the wider community.
The most important technical details
- Favor gRPC communication between a plugin and GitLab Runner.
- Make it possible to version communication interface and support many versions.
- Make Go a primary language for writing plugins but accept other languages too.
Status
Status: RFC.
Who
Proposal:
| Role | Who |
|---|---|
| Authors | Grzegorz Bizon, Tomasz Maczukin |
| Architecture Evolution Coach | Kamil Trzciński |
| Engineering Leader | Elliot Rushton, Cheryl Li |
| Product Manager | Darren Eastman, Jackie Porter |
| Domain Expert / Runner | Arran Walker |
DRIs:
| Role | Who |
|---|---|
| Leadership | Elliot Rushton |
| Product | Darren Eastman |
| Engineering | Tomasz Maczukin |
Domain experts:
| Area | Who |
|---|---|
| Domain Expert / Runner | Arran Walker |