6.9 KiB
| stage | group | info |
|---|---|---|
| Create | Ecosystem | To determine the technical writer assigned to the Stage/Group associated with this page, see https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/engineering/ux/technical-writing/#assignments |
Integrations
Integrations allow you to integrate GitLab with other applications. They are a bit like plugins in that they allow a lot of freedom in adding functionality to GitLab.
Accessing integrations
You can find the available integrations under your project's Settings ➔ Integrations page.
There are more than 20 integrations to integrate with. Click on the one that you want to configure.
Integrations listing
Click on the service links to see further configuration instructions and details.
| Service | Description | Service Hooks |
|---|---|---|
| Asana | Asana - Teamwork without email | No |
| Assembla | Project Management Software (Source Commits Endpoint) | No |
| Atlassian Bamboo CI | A continuous integration and build server | Yes |
| Buildkite | Continuous integration and deployments | Yes |
| Bugzilla | Bugzilla issue tracker | No |
| Campfire | Simple web-based real-time group chat | No |
| Confluence | Replaces the link to the internal wiki with a link to a Confluence Cloud Workspace | No |
| Custom Issue Tracker | Custom issue tracker | No |
| Discord Notifications | Receive event notifications in Discord | No |
| Drone CI | Continuous Integration platform built on Docker, written in Go | Yes |
| Emails on push | Email the commits and diff of each push to a list of recipients | No |
| External Wiki | Replaces the link to the internal wiki with a link to an external wiki | No |
| Flowdock | Flowdock is a collaboration web app for technical teams | No |
| Generic alerts (ULTIMATE) | Receive alerts on GitLab from any source | No |
| GitHub (PREMIUM) | Sends pipeline notifications to GitHub | No |
| Hangouts Chat | Receive events notifications in Google Hangouts Chat | No |
| HipChat | Private group chat and IM | No |
| Irker (IRC gateway) | Send IRC messages, on update, to a list of recipients through an Irker gateway | No |
| Jira | Jira issue tracker | No |
| Jenkins (STARTER) | An extendable open source continuous integration server | Yes |
| JetBrains TeamCity CI | A continuous integration and build server | Yes |
| Mattermost slash commands | Mattermost chat and ChatOps slash commands | No |
| Mattermost Notifications | Receive event notifications in Mattermost | No |
| Microsoft teams | Receive notifications for actions that happen on GitLab into a room on Microsoft Teams using Office 365 Connectors | No |
| Packagist | Update your projects on Packagist, the main Composer repository | Yes |
| Pipelines emails | Email the pipeline status to a list of recipients | No |
| Slack Notifications | Send GitLab events (for example, an issue was created) to Slack as notifications | No |
| Slack slash commands (CORE ONLY) | Use slash commands in Slack to control GitLab | No |
| GitLab Slack application (FREE ONLY) | Use Slack's official application | No |
| PivotalTracker | Project Management Software (Source Commits Endpoint) | No |
| Prometheus | Monitor the performance of your deployed apps | No |
| Pushover | Pushover makes it easy to get real-time notifications on your Android device, iPhone, iPad, and Desktop | No |
| Redmine | Redmine issue tracker | No |
| EWM | EWM work item tracker | No |
| Unify Circuit | Receive events notifications in Unify Circuit | No |
| Webex Teams | Receive events notifications in Webex Teams | No |
| YouTrack | YouTrack issue tracker | No |
Push hooks limit
Introduced in GitLab 12.4.
If a single push includes changes to more than three branches or tags, services
supported by push_hooks and tag_push_hooks events aren't executed.
The number of branches or tags supported can be changed via
push_event_hooks_limit application setting.
Service templates
Service templates are a way to set predefined values for a project integration across all new projects on the instance.
Read more about Service templates.
Project integration management
Project integration management lets you control integration settings across all projects of an instance. On the project level, administrators you can choose whether to inherit the instance configuration or provide custom settings.
Read more about Project integration management.
Troubleshooting integrations
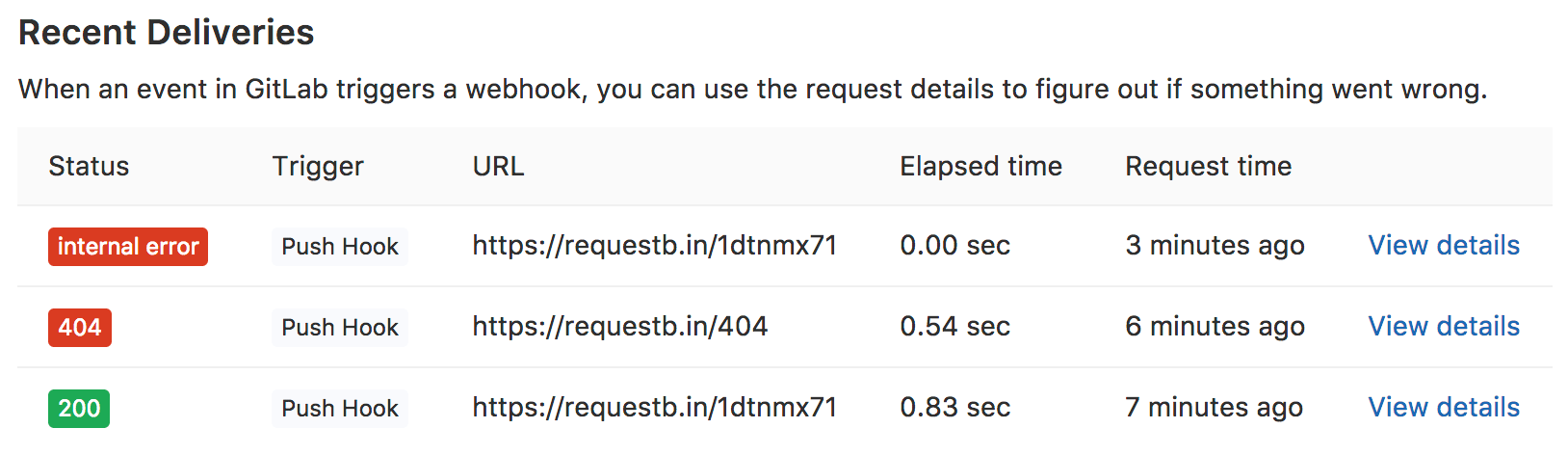
Some integrations use service hooks for integration with external applications. To confirm which ones use service hooks, see the integrations listing above. GitLab stores details of service hook requests made within the last 2 days. To view details of the requests, go to that integration's configuration page.
The Recent Deliveries section lists the details of each request made within the last 2 days:
- HTTP status code (green for 200-299 codes, red for the others,
internal errorfor failed deliveries) - Triggered event
- URL to which the request was sent
- Elapsed time of the request
- Relative time in which the request was made
To view more information about the request's execution, click the respective View details link. On the details page, you can see the request headers and body sent and received by GitLab.
To repeat a delivery using the same data, click Resend Request.
Uninitialized repositories
Some integrations fail with an error Test Failed. Save Anyway when you attempt to set them up on
uninitialized repositories. Some integrations use push data to build the test payload,
and this error occurs when no push events exist in the project yet.
To resolve this error, initialize the repository by pushing a test file to the project and set up the integration again.
Contributing to integrations
Because GitLab is open source we can ship with the code and tests for all plugins. This allows the community to keep the plugins up to date so that they always work in newer GitLab versions.
For an overview of what integrations are available, please see the project_services source directory.
Contributions are welcome!