19 KiB
| stage | group | info | disqus_identifier | type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Verify | Continuous Integration | To determine the technical writer assigned to the Stage/Group associated with this page, see https://about.gitlab.com/handbook/engineering/ux/technical-writing/#assignments | https://docs.gitlab.com/ee/user/project/pipelines/job_artifacts.html | reference, howto |
Job artifacts
Introduced in GitLab 12.4, artifacts in internal and private projects can be previewed when GitLab Pages access control is enabled.
Jobs can output an archive of files and directories. This output is known as a job artifact.
You can download job artifacts by using the GitLab UI or the API.
For an overview, watch the video GitLab CI Pipeline, Artifacts, and Environments. Watch also GitLab CI pipeline tutorial for beginners.
Administrators should review our job artifacts administration documentation.
Define artifacts in the .gitlab-ci.yml file
This example shows how to configure your .gitlab-ci.yml file to create job artifacts:
pdf:
script: xelatex mycv.tex
artifacts:
paths:
- mycv.pdf
expire_in: 1 week
A job named pdf calls the xelatex command to build a PDF file from the
LaTeX source file, mycv.tex.
The paths keyword determines which files to add to the job artifacts.
All paths to files and directories are relative to the repository where the job was created.
The expire_in keyword determines how long GitLab keeps the job artifacts.
You can also use the UI to keep job artifacts from expiring.
If expire_in is not defined, the
instance-wide setting
is used.
For more examples, view the keyword reference for the .gitlab-ci.yml file.
Download job artifacts
You can download job artifacts or view the job archive:
-
On the Pipelines page, to the right of the pipeline:
-
On the Jobs page, to the right of the job:
-
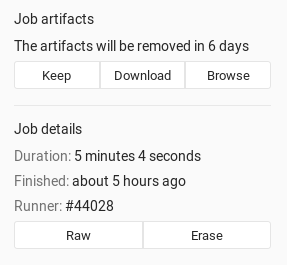
On a job's detail page. The Keep button indicates an
expire_invalue was set: -
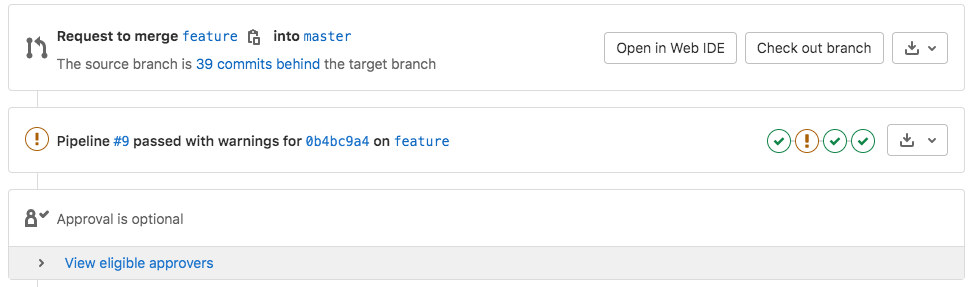
On a merge request, by the pipeline details:
-
When browsing an archive:
If GitLab Pages is enabled in the project, you can preview HTML files in the artifacts directly in your browser. If the project is internal or private, you must enable GitLab Pages access control to preview HTML files.
View failed job artifacts
If the latest job has failed to upload the artifacts, you can see that information in the UI.
Erase job artifacts
WARNING: This is a destructive action that leads to data loss. Use with caution.
You can erase a single job, which also removes the job's artifacts and log. You must be:
- The owner of the job.
- A Maintainer of the project.
To erase a job:
- Go to a job's detail page.
- At the top right of the job's log, select the trash icon.
- Confirm the deletion.
Use GitLab CI/CD to retrieve job artifacts for private projects
To retrieve a job artifact from a different project, you might need to use a private token to authenticate and download the artifact.
The latest job artifacts
Job artifacts created in the most recent successful pipeline for a specific ref are considered the latest artifacts. If you run two types of pipelines for the same ref, timing determines which artifacts are the latest.
For example, if a merge request creates a branch pipeline at the same time as a scheduled pipeline, the pipeline that finished most recently creates the latest job artifact.
In GitLab 13.5 and later, artifacts for parent and child pipelines are searched in hierarchical order from parent to child. For example, if both parent and child pipelines have a job with the same name, the job artifact from the parent pipeline is returned.
Access the latest job artifacts by URL
You can download the latest job artifacts by using a URL.
To download the whole artifacts archive:
https://example.com/<namespace>/<project>/-/jobs/artifacts/<ref>/download?job=<job_name>
To download a single file from the artifacts:
https://example.com/<namespace>/<project>/-/jobs/artifacts/<ref>/raw/<path_to_file>?job=<job_name>
For example, to download the latest artifacts of the job named coverage of
the master branch of the gitlab project that belongs to the gitlab-org
namespace:
https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/jobs/artifacts/master/download?job=coverage
To download the file coverage/index.html from the same artifacts:
https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/jobs/artifacts/master/raw/coverage/index.html?job=coverage
To browse the latest job artifacts:
https://example.com/<namespace>/<project>/-/jobs/artifacts/<ref>/browse?job=<job_name>
For example:
https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/jobs/artifacts/master/browse?job=coverage
There is also a URL for specific files, including HTML files that are shown in GitLab Pages:
https://example.com/<namespace>/<project>/-/jobs/artifacts/<ref>/file/<path>?job=<job_name>
For example, when a job coverage creates the artifact htmlcov/index.html:
https://gitlab.com/gitlab-org/gitlab/-/jobs/artifacts/master/file/htmlcov/index.html?job=coverage
Keep artifacts from most recent successful jobs
- Introduced in GitLab 13.0.
- Feature flag removed in GitLab 13.4.
- Made optional with a CI/CD setting in GitLab 13.8.
By default, the latest job artifacts from the most recent successful jobs are never deleted.
If a job is configured with expire_in,
its artifacts only expire if a more recent artifact exists.
Keeping the latest artifacts can use a large amount of storage space in projects with a lot of jobs or large artifacts. If the latest artifacts are not needed in a project, you can disable this behavior to save space:
- Go to the project's Settings > CI/CD > Artifacts.
- Clear the Keep artifacts from most recent successful jobs checkbox.
You can disable this behavior for all projects on a self-managed instance in the instance's CI/CD settings.
When you disable the feature, the latest artifacts do not immediately expire. A new pipeline must run before the latest artifacts can expire and be deleted.
artifacts:reports
- Introduced in GitLab 11.2.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.2 and above.
The artifacts:reports keyword is used for collecting test reports, code quality
reports, and security reports from jobs. It also exposes these reports in the GitLab
UI (merge requests, pipeline views, and security dashboards).
The test reports are collected regardless of the job results (success or failure).
You can use artifacts:expire_in to set up an expiration
date for their artifacts.
If you also want the ability to browse the report output files, include the
artifacts:paths keyword.
artifacts:reports:junit
- Introduced in GitLab 11.2.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.2 and above.
The junit report collects JUnit report format XML files
as artifacts. Although JUnit was originally developed in Java, there are many
third party ports for other
languages like JavaScript, Python, Ruby, and so on.
See Unit test reports for more details and examples. Below is an example of collecting a JUnit report format XML file from Ruby's RSpec test tool:
rspec:
stage: test
script:
- bundle install
- rspec --format RspecJunitFormatter --out rspec.xml
artifacts:
reports:
junit: rspec.xml
The collected Unit test reports upload to GitLab as an artifact and display in merge requests.
If the JUnit tool you use exports to multiple XML files, specify
multiple test report paths within a single job to
concatenate them into a single file. Use a filename pattern (junit: rspec-*.xml),
an array of filenames (junit: [rspec-1.xml, rspec-2.xml, rspec-3.xml]), or a
combination thereof (junit: [rspec.xml, test-results/TEST-*.xml]).
artifacts:reports:dotenv
- Introduced in GitLab 12.9.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and later.
The dotenv report collects a set of environment variables as artifacts.
The collected variables are registered as runtime-created variables of the job, which is useful to set dynamic environment URLs after a job finishes.
There are a couple of exceptions to the original dotenv rules:
- The variable key can contain only letters, digits, and underscores (
_). - The maximum size of the
.envfile is 5 KB. - In GitLab 13.5 and older, the maximum number of inherited variables is 10.
- In GitLab 13.6 and later, the maximum number of inherited variables is 20.
- Variable substitution in the
.envfile is not supported. - The
.envfile can't have empty lines or comments (starting with#). - Key values in the
envfile cannot have spaces or newline characters (\n), including when using single or double quotes. - Quote escaping during parsing (
key = 'value'->{key: "value"}) is not supported.
artifacts:reports:cobertura
- Introduced in GitLab 12.9.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
The cobertura report collects Cobertura coverage XML files.
The collected Cobertura coverage reports upload to GitLab as an artifact
and display in merge requests.
Cobertura was originally developed for Java, but there are many third party ports for other languages like JavaScript, Python, Ruby, and so on.
artifacts:reports:terraform
- Introduced in GitLab 13.0.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
The terraform report obtains a Terraform tfplan.json file. JQ processing required to remove credentials. The collected Terraform
plan report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and displays
in merge requests. For more information, see
Output terraform plan information into a merge request.
artifacts:reports:codequality
- Introduced in GitLab Starter 11.5.
- Made available in all tiers in GitLab 13.2.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
The codequality report collects Code Quality issues
as artifacts.
The collected Code Quality report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and is summarized in merge requests.
artifacts:reports:sast
- Introduced in GitLab 11.5.
- Made available in all tiers in GitLab 13.3.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
The sast report collects SAST vulnerabilities
as artifacts.
The collected SAST report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and is summarized in merge requests and the pipeline view. It's also used to provide data for security dashboards.
artifacts:reports:secret_detection
- Introduced in GitLab 13.1.
- Made available in all tiers in GitLab 13.3.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
The secret-detection report collects detected secrets
as artifacts.
The collected Secret Detection report is uploaded to GitLab as an artifact and summarized in the merge requests and pipeline view. It's also used to provide data for security dashboards.
artifacts:reports:dependency_scanning (ULTIMATE)
- Introduced in GitLab 11.5.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
The dependency_scanning report collects Dependency Scanning vulnerabilities
as artifacts.
The collected Dependency Scanning report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and is summarized in merge requests and the pipeline view. It's also used to provide data for security dashboards.
artifacts:reports:container_scanning (ULTIMATE)
- Introduced in GitLab 11.5.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
The container_scanning report collects Container Scanning vulnerabilities
as artifacts.
The collected Container Scanning report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and is summarized in merge requests and the pipeline view. It's also used to provide data for security dashboards.
artifacts:reports:dast (ULTIMATE)
- Introduced in GitLab 11.5.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
The dast report collects DAST vulnerabilities
as artifacts.
The collected DAST report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and is summarized in merge requests and the pipeline view. It's also used to provide data for security dashboards.
artifacts:reports:api_fuzzing (ULTIMATE)
- Introduced in GitLab 13.4.
- Requires GitLab Runner 13.4 or later.
The api_fuzzing report collects API Fuzzing bugs
as artifacts.
The collected API Fuzzing report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and is summarized in merge requests and the pipeline view. It's also used to provide data for security dashboards.
artifacts:reports:coverage_fuzzing (ULTIMATE)
- Introduced in GitLab 13.4.
- Requires GitLab Runner 13.4 or later.
The coverage_fuzzing report collects coverage fuzzing bugs
as artifacts.
The collected coverage fuzzing report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and is summarized in merge requests and the pipeline view. It's also used to provide data for security dashboards.
artifacts:reports:license_management (ULTIMATE)
- Introduced in GitLab 11.5.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
WARNING: This artifact is still valid but is deprecated in favor of the artifacts:reports:license_scanning introduced in GitLab 12.8.
The license_management report collects Licenses
as artifacts.
The collected License Compliance report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and is summarized in merge requests and the pipeline view. It's also used to provide data for security dashboards.
artifacts:reports:license_scanning (ULTIMATE)
- Introduced in GitLab 12.8.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
The license_scanning report collects Licenses
as artifacts.
The License Compliance report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and displays automatically in merge requests and the pipeline view, and provide data for security dashboards.
artifacts:reports:performance (PREMIUM)
- Introduced in GitLab 11.5.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
The performance report collects Browser Performance Testing metrics
as artifacts.
The collected Browser Performance report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and displays in merge requests.
artifacts:reports:load_performance (PREMIUM)
- Introduced in GitLab 13.2 in GitLab Premium 13.2.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
The load_performance report collects Load Performance Testing metrics
as artifacts.
The report is uploaded to GitLab as an artifact and is shown in merge requests automatically.
artifacts:reports:metrics (PREMIUM)
Introduced in GitLab 11.10.
The metrics report collects Metrics
as artifacts.
The collected Metrics report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and displays in merge requests.
artifacts:reports:requirements (ULTIMATE)
- Introduced in GitLab 13.1.
- Requires GitLab Runner 11.5 and above.
The requirements report collects requirements.json files as artifacts.
The collected Requirements report uploads to GitLab as an artifact and existing requirements are marked as Satisfied.
Troubleshooting job artifacts
Error message No files to upload
This is often preceded by other errors or warnings that specify the filename and why it wasn't generated in the first place. Please check the entire job log for such messages.
If you find no helpful messages, please retry the failed job after activating CI/CD debug logging. This provides useful information to investigate further.