1.9 KiB
1.9 KiB
Command Line basic commands
Start working on your project
-
In Git, when you copy a project you say you "clone" it. To work on a git project locally (from your own computer), you will need to clone it. To do this, start by signing in at GitLab.com.. To do it, go to your gitlab.com account
-
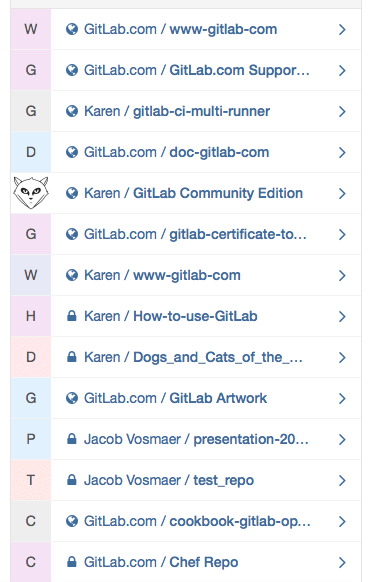
When you are on your Dashboard, click on the project that you'd like to clone, which you'll find at the right side of your screen
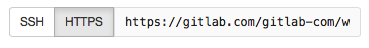
- To work in the project, you can copy a link to the Git repository through a SSH or a HTTPS protocol. SSH is easier to use after it's been setup. When you're in the project, click on the HTTPS or SSH button at the right side of your screen. Then copy the link (you'll have to paste it on your shell in the next step)
On the command line
- To clone your project, go to your computer's shell and type the following command
git clone PASTE HTTPS OR SSH HERE
A clone of the project will be created in your computer
It's important to know some basic commands to work on your shell
- Go into a project, directory or file to work in it
cd NAME-OF-PROJECT-OR-FILE
- Go back one directory or file
cd ../
- To see what’s in the directory that you are in
ls
- Create a directory
mkdir NAME-OF-YOUR-DIRECTORY
- Create a README.md or file in directory
touch README.md
nano README.md
#### ADD YOUR INFORMATION
#### Press: control + X
#### Type: Y
#### Press: enter
- Remove a file
rm NAME-OF-FILE
- Remove a directory and all of its contents
rm -rf NAME-OF-DIRECTORY
- View history in the command line
history
- Carry out commands for which the account you are using lacks authority. (You will be asked for an administrator’s password)
sudo