11 KiB
Introduction to environments and deployments
Note: Introduced in GitLab 8.9.
During the development of software, there can be many stages until it's ready for public consumption. You sure want to first test your code and then deploy it in a testing or staging environment before you release it to the public. That way you can prevent bugs not only in your software, but in the deployment process as well.
GitLab CI is capable of not only testing or building your projects, but also deploying them in your infrastructure, with the added benefit of giving you a way to track your deployments. In other words, you can always know what is currently being deployed or has been deployed on your servers.
Overview
With environments, you can control the Continuous Deployment of your software
all within GitLab. All you need to do is define them in your project's
.gitlab-ci.yml as we will explore below. GitLab provides a full
history of your deployments per every environment.
Environments are like tags for your CI jobs, describing where code gets deployed. Deployments are created when jobs deploy versions of code to environments, so every environment can have one or more deployments. GitLab keeps track of your deployments, so you always know what is currently being deployed on your servers.
To better understand how environments and deployments work, let's consider an example. We assume that you have already created a project in GitLab and set up a Runner. The example will cover the following:
- We are developing an application
- We want to run tests and build our app on all branches
- Our default branch is
master - We deploy the app only when a pipeline on
masterbranch is run
Let's see how it all ties together.
Defining environments
Let's consider the following .gitlab-ci.yml example:
stages:
- test
- build
- deploy
test:
stage: test
script: echo "Running tests"
build:
stage: build
script: echo "Building the app"
deploy_staging:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Deploy to staging server"
environment:
name: staging
url: https://staging.example.com
only:
- master
We have defined 3 stages:
- test
- build
- deploy
The jobs assigned to these stages will run in this order. If a job fails, then
the builds that are assigned to the next stage won't run, rendering the pipeline
as failed. In our case, the test job will run first, then the build and
lastly the deploy_staging. With this, we ensure that first the tests pass,
then our app is able to be built successfully, and lastly we deploy to the
staging server.
The environment keyword is just a hint for GitLab that this job actually
deploys to this environment's name. It can also have a url which, as we
will later see, is exposed in various places within GitLab. Each time a job that
has an environment specified and succeeds, a deployment is recorded, remembering
the Git SHA and environment name.
To sum up, with the above .gitlab-ci.yml we have achieved that:
- All branches will run the
testandbuildjobs. - The
deploy_stagingjob will run only on themasterbranch which means all merge requests that are created from branches don't get to deploy to the staging server - When a merge request is merged, all jobs will run and the
deploy_stagingin particular will deploy our code to a staging server while the deployment will be recorded in an environment namedstaging.
Let's now see how that information is exposed within GitLab.
Viewing the current status of an environment
The environment list under your project's Pipelines ➔ Environments, is where you can find information of the last deployment status of an environment.
Here's how the Environments page looks so far.
There's a bunch of information there, specifically you can see:
- The environment's name with a link to its deployments
- The last deployment ID number and who performed it
- The build ID of the last deployment with its respective job name
- The commit information of the last deployment such as who committed, to what branch and the Git SHA of the commit
- The exact time the last deployment was performed
- A button that takes you to the URL that you have defined under the
environmentkeyword in.gitlab-ci.yml - A button that re-deploys the latest deployment, meaning it runs the job defined by the environment name for that specific commit
Notes:
- While you can create environments manually in the web interface, we recommend
that you define your environments in
.gitlab-ci.ymlfirst. They will be automatically created for you after the first deploy. - The environments page can only be viewed by Reporters and above. For more information on the permissions, see the permissions documentation.
- Only deploys that happen after your
.gitlab-ci.ymlis properly configured will show up in the "Environment" and "Last deployment" lists.
The information shown in the Environments page is limited to the latest deployments, but as you may have guessed an environment can have multiple deployments.
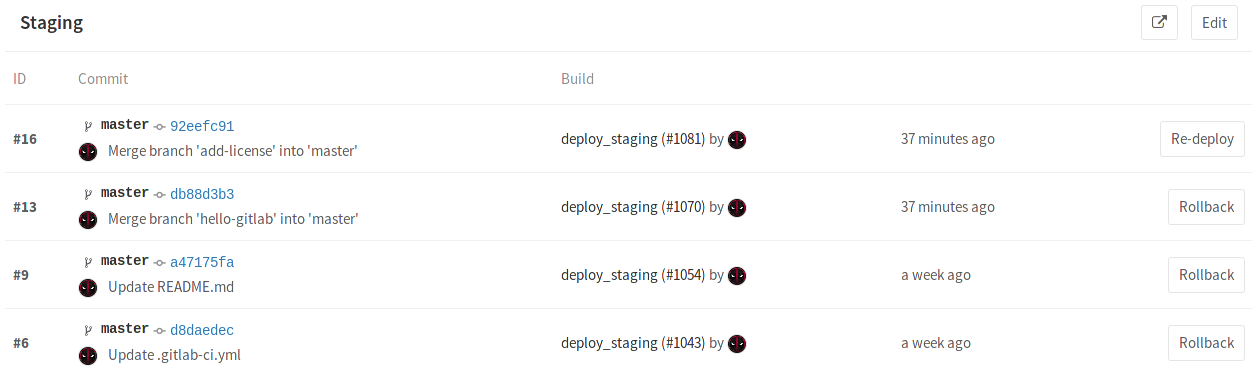
Viewing the deployment history of an environment
GitLab keeps track of your deployments, so you always know what is currently being deployed on your servers. That way you can have the full history of your deployments per every environment right in your browser. Clicking on an environment will show the history of its deployments. Assuming you have deployed multiple times already, here's how a specific environment's page looks like.
We can see the same information as when in the Environments page, but this time all deployments are shown. As you may have noticed, apart from the Re-deploy button there are now Rollback buttons for each deployment. Let's see how that works.
Rolling back changes
You can't control everything, so sometimes things go wrong. When that unfortunate
time comes GitLab has you covered. Simply by clicking the Rollback button
that can be found in the deployments page
(Pipelines ➔ Environments ➔ environment name) you can relaunch the
job with the commit associated with it.
Note: Bare in mind that your mileage will vary and it's entirely up to how you define the deployment process in the job's
scriptwhether the rollback succeeds or not. GitLab CI is just following orders.
Thankfully that was the staging server that we had to rollback, and since we learn from our mistakes, we decided to not make the same again when we deploy to the production server. Enter manual actions for deployments.
Manually deploying to environments
Turning a job from running automatically to a manual action is as simple as
adding when: manual to it. To expand on our previous example, let's add
another job that this time deploys our app to a production server and is
tracked by a production environment. The .gitlab-ci.yml looks like this
so far:
stages:
- test
- build
- deploy
test:
stage: test
script: echo "Running tests"
build:
stage: build
script: echo "Building the app"
deploy_staging:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Deploy to staging server"
environment:
name: staging
url: https://staging.example.com
only:
- master
deploy_prod:
stage: deploy
script:
- echo "Deploy to production server"
environment:
name: production
url: https://example.com
when: manual
only:
- master
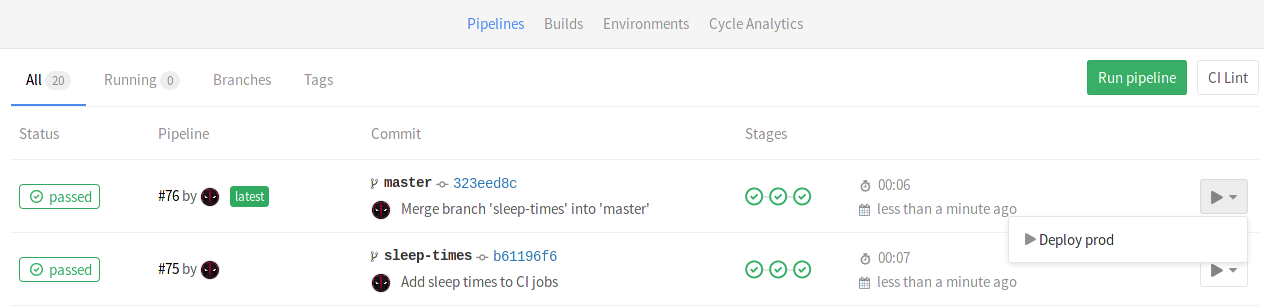
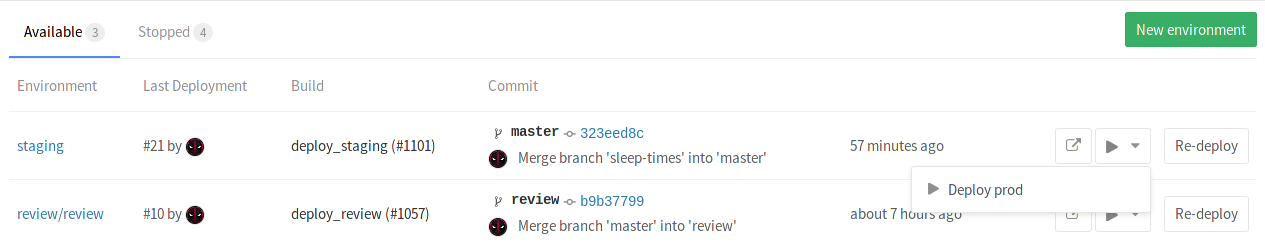
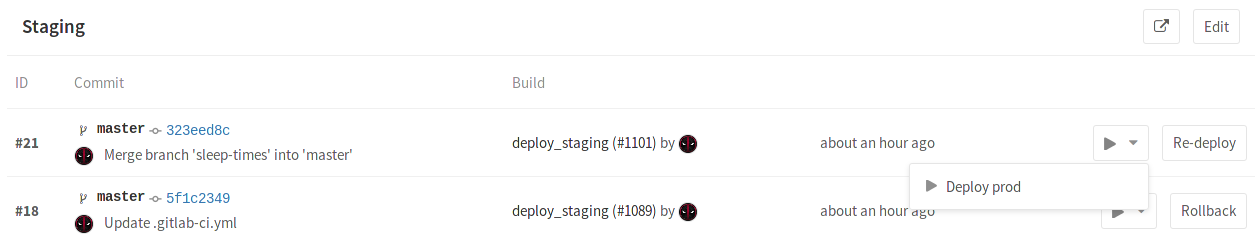
The when: manual action exposes a play button in GitLab's UI and the
deploy_prod job will only be triggered if and when we click that play button.
You can find it in the pipeline, build, environment, and deployment views.
| Pipelines | Single pipeline | Environments | Deployments | Builds |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Clicking on the play button in either of these places will trigger the
deploy_prod job, and the deployment will be recorded under a new
environment named production.
While this is fine for deploying to some stable environments like staging or
production, what happens for branches? So far we haven't defined anything
regarding deployments for branches other than master. Dynamic environments
will help us achieve that.
Dynamic environments
As the name suggests, it is possible to create environments on the fly by just
declaring their names dynamically in .gitlab-ci.yml.
GitLab Runner exposes various environment variables when a job runs, and as such you can use them
review:
stage: deploy
script:
- rsync -av --delete public /srv/nginx/pages/$CI_BUILD_REF_NAME
environment:
name: review/$CI_BUILD_REF_NAME
url: https://$CI_BUILD_REF_NAME.example.com
Closing an environment
review:
stage: deploy
script:
- rsync -av --delete public /srv/nginx/pages/$CI_BUILD_REF_NAME
environment:
name: review/$CI_BUILD_REF_NAME
url: http://$CI_BUILD_REF_NAME.$APPS_DOMAIN
on_stop: stop_review
stop_review:
script: rm -rf /srv/nginx/pages/$CI_BUILD_REF_NAME
when: manual
environment:
name: review/$CI_BUILD_REF_NAME
action: stop
Checkout deployments locally
Since 8.13, a reference in the git repository is saved for each deployment. So
knowing what the state is of your current environments is only a git fetch
away.
In your git config, append the [remote "<your-remote>"] block with an extra
fetch line:
fetch = +refs/environments/*:refs/remotes/origin/environments/*
Further reading
Below are some links you may find interesting:
- The
.gitlab-ci.ymldefinition of environments - A blog post on Deployments & Environments
- Review Apps Expand dynamic environments to deploy your code for every branch
TODO
Actions
- View environments +
- View deployments +
- Rollback deployments +
- Run deployments +
- View link to environment URL
- View last commit message of deployment +
- View person who performed the deployment +
- View commit SHA that triggered the deployment +
- View branch the deployment was based on +
- View time ago the deployment was performed +